When did I learn about GitFlow?
I learnt about GitFlow during my placement at 3squared, as it was the agreed method for managing branches across the different products and teams. As placement students we had to fully understand how GitFlow worked before we could start working on any of the companies products.
Why is GitFlow helpful?
GitFLow helps large teams manage new features, deployments, hotfixes and ensuring there is a chain-of-command in respect of code moving between branches.
How does GitFlow work?
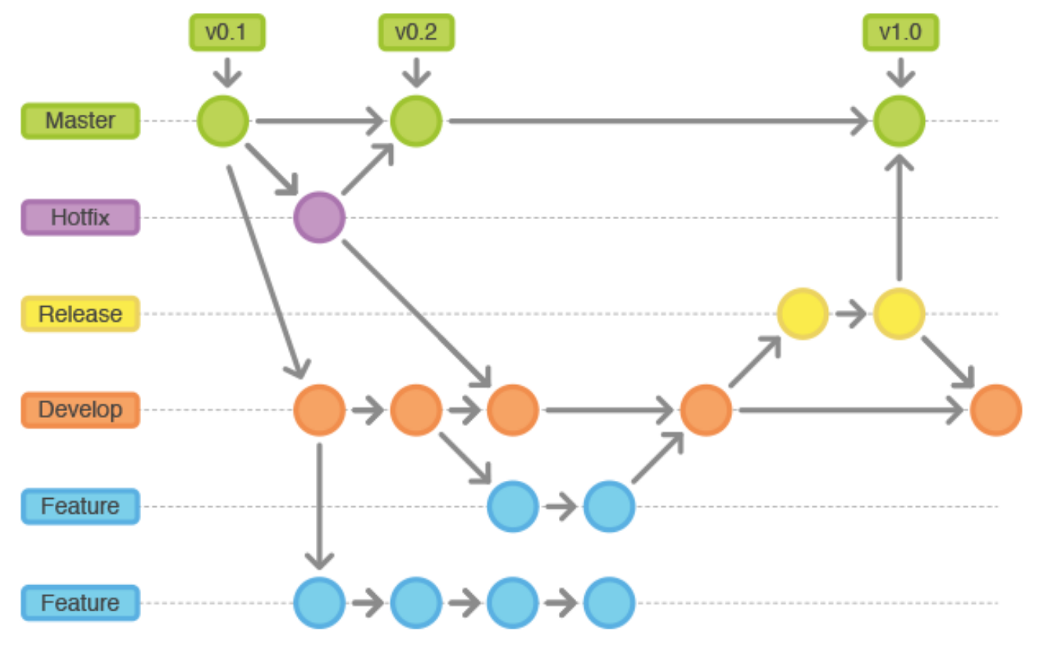 Image from Medium
Image from Medium
The branches
master: This branch mirrors the state of the deployed environment.develop: This branch contains a collection of all the most up to date features.feature/*: These branches are based offdevelopand are where the new changes are written, before being merged back intodevelop.release/*: These branches are based offdevelopand are where you make final config changes ready to be deployed to a specific environment prior to being merged intomaster.hotfix/*: These branches are based offmasterto make quick fixes that can be quickly be merged back intomasterto be deployed.
Starting a new feature
You’ve just been assigned a ticket and it’s time to start coding! You will want to create a new feature branch based off develop. For example feature/add-profile-page. Put all your commits and changes related to a given ticket/workload on this branch. Once you have finished your changes open a pull request from your feature branch to develop.
When doing feature work you will simply by winding in and out of develop.
Code reviewing
Whenever work wants to be moved onto the develop branch it must be peer reviewed by a senior developer. As a junior developer this is great because you can receive feedback but it also ensures code style is maintained and no glaring issues are introduced. It also means code can enter the the develop branch without people knowing about it!
Deployments
There is now a collection of tickets on the develop branch ready to be deployed. At this point a new release branch will be made such as release/001.002.000 based off develop. On this branch you can make final config changes such as changing database connection strings to live ones rather than local ones.
Once this is ready you should merge the release branch into master and perform your deployment.
Hotfixes
If there are any issues on production environment and you need a quicker fix than following the ‘feature -> develop -> release -> master’ route, you can make a hotfix branch. Eg. hotfix/001.002.001. In this branch you can make brief changes and quickly get them deployed.
This hotfix branch should be merged into master to be deployed, and back into develop to ensure your changes don’t get lost.
More information
You can read more about GitFlow in this Atlassian guide